DIABETES MELLIETUS
Causes:
It is due to the person having high blood sugar either because the body does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced.The main symptoms are listed below,
Symptoms:-
- POLYURIA (FREQUENT URINATION)
- POLYDIPSIA(
INCREASED THRIST)
- POLYPHAGIA(INCREASED HUNGER)
Please take deep look at the photograph given below,
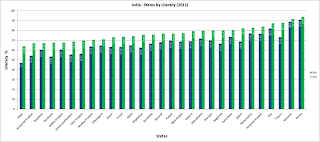
GLOBAL RATIO:-
GUIDELINES TO BE FOLLOWED:-
Here are some suggestions for minimizing sugar spikes:
1. Eat soluble fiber
Soluble fiber interferes with carbohydrate absorption from the intestines into your bloodstream. By limiting absorption, less sugar enters the blood and prevents spikes.
We suggest supplementing with psyllium husk or beta-glucan 10 to 20 minutes before each major meal. Both of these soluble fibers come in powder form and mix well with water.
2. Take chromiun Polynicotinate
Diabetic diet guidelines most direct people to take chromium polynicotinate, a trace mineral that enhances the effect of insulin.
With chromium present, cells don't needs as much insulin to uptake glucose. The more sensitive the cells are to insulin, the less is released into the blood.
Take 500 mcg of chromium polynicotinate with each major meal.
3. Try coffee berry & cinnamon
Cinnamon is well known by naturopathic doctors for its positive effects on blood sugar. The problem is that whole cinnamon contains oils that prevent it from working.
The best suggestion is to take 200 mg with each meal of a water-based cinnamon extract free from the oils.
Cinnamon works better with the herb coffee berry. Coffee berry inhibits the conversion of glycogen (stored sugar) to blood glucose, thus helping to minimize spikes. About 50 mg of coffee berry with each meal should do the trick.
4. Eat complex carbhohydrates
Complex carbs have less effect on blood sugar spikes. Foods like oatmeal, bran, wheatgerm, and whole grain breads take longer to breakdown to glucose. The long it takes to breakdown carbs to glucose, the less insulin is released.
A word of warning: all carbohydrates, complex or not, eventually become glucose and will raise blood sugar levels. We suggest cutting the servings breads and cereals in half.
5. Drink Apple Cider Vinegar
Drinking apple cider vinegar can also help to lower blood sugar levels. Supplement with 1 ounce before meals heavy in carbohydrates.
 Restore Insulin Sensitivity
Restore Insulin Sensitivity
The diabetic diet guidelines would not be complete without learning how to restore insulin sensitivity. When the cells in your body become resistant to insulin, hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) sets in.
We suggest the following to help restore insulin sensitivity:
1. Take lipoic acid
Glucose (blood sugar) destroys the insulin receptors sticking out from cell membranes. Without the receptors, insulin can not work.
Lipoic acid is a naturally occurring antioxidant that protects insulin receptors. We suggest taking 200 to 300 mg/day of R-lipoic acid (the "R" form is more potent).
2. Take MORE Chromium
A study of type 2 diabetics compared two forms of chromium (brewer's yeast and chromium chloride). Both forms of chromium significantly improved blood sugar control by promoting the uptake of glucose into the tissues after eating a carbohydrate rich meal.
Fasting blood glucose levels were also lowered during a 2 month follow-up period. Foods rich in chromium include (in order of most to least):
- Egg yolk
- Brewer's yeast
- Breads (whole grain, wheat, sprouted, rye)
- Apples
- Spinach
- Oranges
 Reduce Oxidative Stress
Reduce Oxidative Stress
Excess blood sugar creates extreme levels of oxidative stress, one of the leading theories of aging. If not properly metabolized, blood sugar quickly transforms into highly reactive molecules that damage your body.
Reducers, also known as antioxidants, are foods that lower oxidative stress by mopping up reactive sugar metabolites.
Eating a wide variety of antioxidants from a wide variety of sources is a key step for beating diabetes.
The following foods are rich in reducers (antioxidants) and should make up a large part of diabetic diets:
1. Red beans
2. Blueberries
3. Cranberries
4. Artichokes
5. Pomegranate
6. Green & black tea
7. Cocoa (dark chocolate)
8. Tart cherries
9. Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli)
Every meal should contain 2-3 servings of reducers (antioxidants). And if you got to snack, eat only foods rich in antioxidants.
 Prevent Glycation
Prevent Glycation
Glycation (defined as sugar molecules reacting with proteins to produce nonfunctional structures in the body) is a key feature of diabetes-related complications.
It's a dangerous reaction that compromises proteins throughout the body and is linked to nerve damage, heart attacks, strokes, and blindness.
Protectors are foods that can minimize the effects of glycation:
1. Turkey
2. Liver
3. Tuna
4. Chili peppers
5. Lentils
6. Chicken
7. Lean red meat
Chili peppers added to marinades for chicken and fish is a great way to enhance diabetic diets.
 Support a Healthy Metabolic Rate
Support a Healthy Metabolic Rate
A healthy metabolic rate wraps-up our diabetic diet guidelines. Burning body fat and calories while resting is a great way to not only lose weight, but also improve blood sugar levels.
We suggest the following nutrients for restoring a healthy metabolic rate:
1. Green tea
2. Brown Seaweed (fucoxanthin, bladderwhack)
3. Exercise (specifically muscle toning exercises)
Summary
The diabetic diet guidelines are essential if you are to beat diabetes. Incorporate them into any diabetic diet that you follow for optimal results.
"So the next time when you see you a diabetic person,do tell him to follow these things!!!"
For more details:-
Visit.www.medicinenet.com